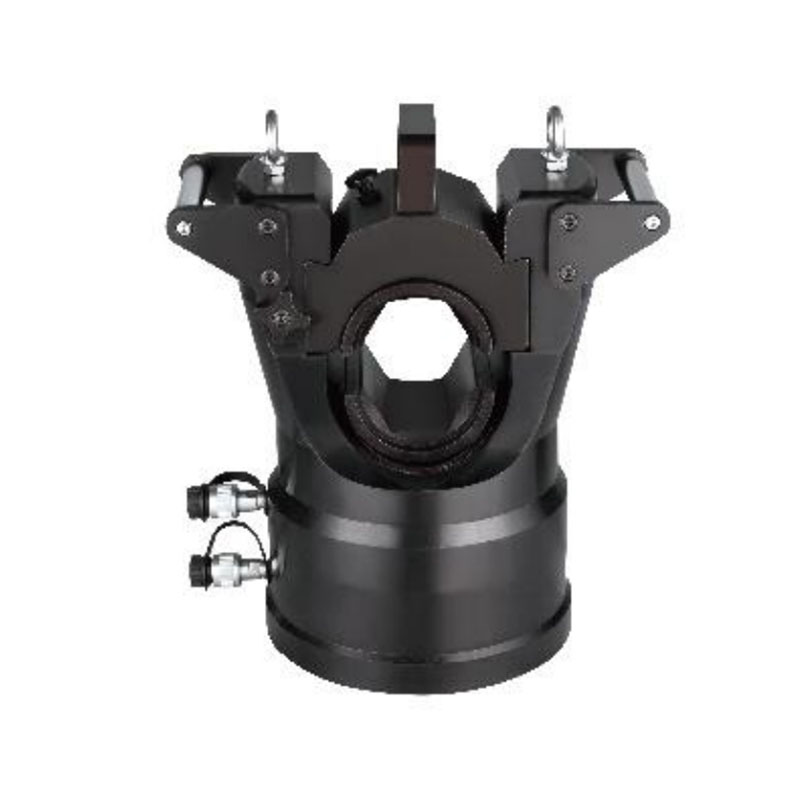
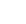
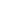
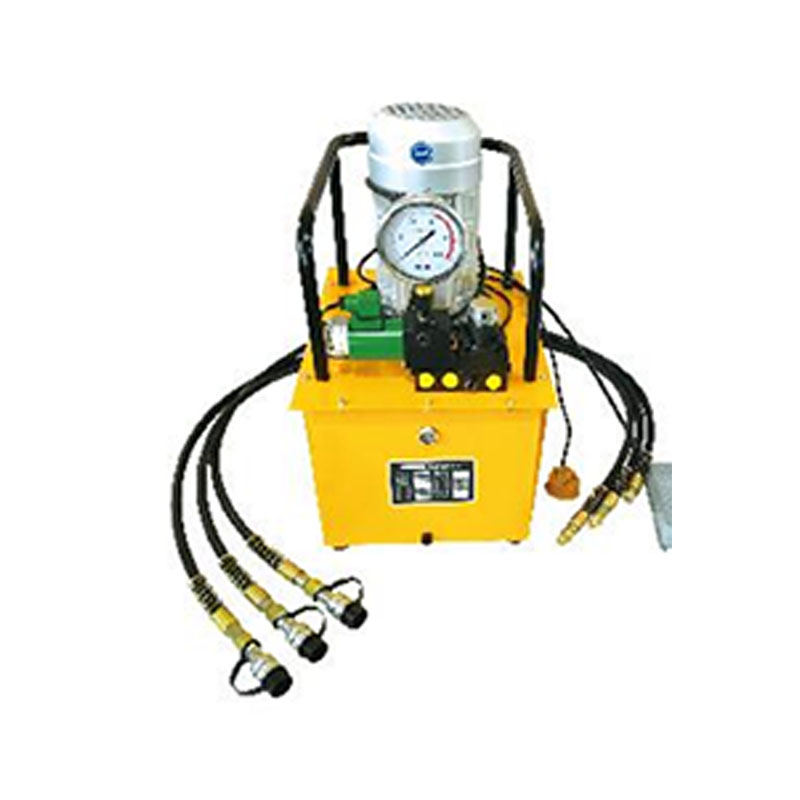
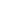ZCB-700AB-3 three oil solenoid valve electric hydraulic pump 70Mpa ultra-high pressure electric pump
 2025.06.13
2025.06.13
 Industry News
Industry News
Environmental temperature plays a significant role in the performance and reliability of many mechanical systems, and hydraulic pumps are no exception. Whether operating in freezing climates or scorching industrial environments, temperature can influence the efficiency, durability, and responsiveness of hydraulic systems. Understanding how a hydraulic pump behaves under such conditions is vital for system designers, operators, and maintenance personnel.

Temperature Effects on Hydraulic Fluid Properties
Hydraulic pumps rely heavily on the characteristics of hydraulic fluid to function properly. One of the primary concerns in cold temperatures is how the fluid’s viscosity changes. At very low temperatures, hydraulic fluid thickens, increasing resistance and making it harder for the pump to circulate fluid effectively. This can cause sluggish system response, cavitation, or even failure to start.
Conversely, in high-temperature environments, hydraulic fluid becomes thinner and loses its lubricating qualities. This can result in increased internal leakage, reduced system pressure, and accelerated wear of internal pump components. If the temperature continues to rise beyond the fluid’s operating range, oxidation and degradation can occur, causing sludge formation and clogged filters.
Seal and Material Degradation
The materials used in hydraulic pumps—including seals, gaskets, and housing components—are also affected by temperature. At low temperatures, seals may become brittle, increasing the likelihood of cracks or leaks. In high-temperature environments, elastomer seals may soften or swell, losing their effectiveness over time.
Additionally, thermal expansion and contraction of metal components can cause dimensional changes that affect the pump’s internal tolerances. Over time, repeated exposure to these conditions can cause reduced mechanical efficiency and potential misalignment within the pump.
Start-Up Challenges in Cold Climates
One of the challenging scenarios for a hydraulic pump is cold start-up in low-temperature environments. The thicker fluid and reduced elasticity of components can significantly increase the load on the motor driving the pump. Cold starts may result in delayed fluid circulation, erratic system behavior, or damage to pump parts due to inadequate lubrication at the start.
To mitigate these issues, many systems incorporate preheating mechanisms, such as block heaters or fluid warmers, to bring components and fluid to an acceptable operating temperature before activation.
Heat Management and Cooling Solutions
In high-temperature applications, effective heat management is essential to maintaining stable performance. Hydraulic pumps are often paired with heat exchangers or oil coolers that regulate fluid temperature and prevent thermal overload. Choosing a pump with a suitable temperature range and ensuring proper ventilation in enclosed spaces can also reduce the impact of excessive heat.
Monitoring fluid temperature during operation allows for early detection of overheating. Automated shutdown systems or alarms can help prevent damage due to thermal stress, preserving the longevity of both the pump and the entire hydraulic system.
Selecting the Right Pump for the Environment
Manufacturers offer specialized hydraulic pumps designed for cold-temperature applications. These may include pumps with high-grade seals, temperature-resistant materials, and compatibility with synthetic hydraulic fluids engineered for stable performance in both hot and cold environments.
Selecting a hydraulic pump that matches the specific temperature requirements of the working environment is essential for maintaining consistent output, reducing maintenance, and preventing premature failure.
Conclusion
Bad temperatures—whether high or low—can significantly affect the performance and longevity of a hydraulic pump. From fluid viscosity changes to material degradation, the challenges posed by temperature require careful consideration in pump selection, system design, and maintenance strategies. By addressing these factors proactively, it is possible to ensure stable, efficient performance even under harsh environmental conditions.



 Español
Español русский
русский