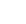
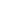
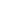P-464 dual oil manual hydraulic pump high-pressure pump 70Mpa, 7L large oil tank manual pump
 2025.06.20
2025.06.20
 Industry News
Industry News
In many industrial and mobile hydraulic systems, the hydraulic pump is the central component responsible for delivering the power necessary to perform demanding tasks. When operating under heavy load conditions, the performance of the pump becomes a critical determinant of overall system efficiency, responsiveness, and reliability. This article explores how a hydraulic pump performs under such high-stress scenarios and what factors influence its behavior and longevity.

Understanding Heavy Load Conditions
Heavy load conditions refer to operating scenarios where the hydraulic system must deliver high pressure and flow consistently to drive large actuators, lift heavy materials, or operate large-scale machinery. These conditions are common in industries such as construction, mining, steel production, and large agricultural equipment. The pump must supply continuous and powerful hydraulic energy without losing efficiency or overheating.
Key Performance Factors Under Heavy Load
When a hydraulic pump operates under a heavy load, its internal components—such as pistons, vanes, gears, and seals—are subjected to elevated mechanical and thermal stress. A key performance indicator in these scenarios is volumetric efficiency, which measures the pump’s ability to maintain flow rate under pressure. High-quality pumps can sustain a high volumetric efficiency even when pressure demands increase, ensuring the system performs as required.
Another important metric is mechanical efficiency, which relates to how much energy is lost to friction and internal leakage. Under heavy load, lower-quality pumps may exhibit increased internal leakage or mechanical drag, reducing output and wasting energy. Performing pumps are designed to maintain internal friction and tight tolerances to reduce energy loss.
Material Strength and Construction Design
The performance of a hydraulic pump under heavy-duty use heavily depends on its construction. Pumps made from high-grade, heat-treated steel or specialized alloys exhibit better resistance to fatigue and wear. Reinforced housings, precision-machined components, and hardened sealing surfaces ensure the pump can handle continuous high-pressure operation without failure.
In addition, pumps designed for heavy loads often incorporate advanced bearing systems and internal balancing mechanisms that reduce wear and vibration during prolonged operation. This design stability contributes directly to both performance and pump longevity.
Heat Generation and Thermal Management
One major consequence of operating under heavy load is increased heat generation. As pressure and friction rise within the pump, so does temperature. Excessive heat can cause premature oil breakdown, reduced lubrication, and damage to seals and internal surfaces. Therefore, thermal management becomes essential.
Systems designed for heavy-duty applications typically include external coolers or heat exchangers that dissipate excess heat. Some pumps also feature integrated cooling channels or are paired with oil reservoirs designed to enhance heat dissipation. Without adequate cooling, even the robust hydraulic pump will eventually suffer from performance degradation or mechanical failure.
Monitoring and Maintenance Considerations
When a hydraulic pump is regularly exposed to high-load conditions, proactive monitoring is necessary. Temperature sensors, pressure gauges, and flow monitors provide real-time feedback on the pump’s condition and help detect anomalies before they escalate into major failures.
Scheduled maintenance becomes even more critical under heavy loads. Regular oil analysis, seal inspections, and wear measurements help ensure the pump continues to operate at good efficiency. Ignoring these maintenance routines can quickly reduce the lifespan of even the engineered pumps.
Conclusion
A hydraulic pump operating under heavy load conditions must deliver consistent pressure, maintain mechanical and volumetric efficiency, and withstand significant thermal and mechanical stress. With the right materials, design features, and thermal management systems, many modern pumps are capable of performing reliably under such demanding conditions. However, regular monitoring and maintenance are key to ensuring long-term durability and preventing costly downtime. Selecting a pump specifically designed for heavy-duty applications is essential for ensuring system reliability and operational success.



 Español
Español русский
русский